Blog posts flood the internet each day, yet many look and sound the same. Search engines spot copied lines. Readers feel bored when every paragraph follows an obvious pattern. Even smart tools now flag lines that appear machine-written.
A writer who hopes to stand out must break those habits early. One fast way is to check your paper for ai before hitting publish.
The scan shows repeated phrases, stiff wording, and odd rhythms. With that early warning, changes can happen while ideas remain fresh. This article maps out clear steps for avoiding duplicate and AI-like patterns in both markup and copy. Each part speaks in plain language, like a chat at a kitchen table. By the end, any blogger, teacher, or business owner will have a solid plan.
The goal is simple: keep posts lively, human, and helpful while staying friendly with search rules. Now, let the journey toward cleaner content begin.
Why Duplicate Patterns Hurt Blogs
Search engines rank pages by judging value and freshness. When a blog repeats sentence stems, meta tags, or heading layouts, the code whispers, “nothing new here”. Crawlers then push the post down the results page, even if the tips inside are helpful. Duplicate patterns also harm trust with real readers.

People skim quickly; they spot overused phrases like “in conclusion”, “ultimate guide”, or “keep reading” stacked the same way in every entry. Soon they believe the site is managed by a robot, not a caring author. That feeling lowers time on page and cuts shares.
💵Sponsors notice the dip and may walk away. In classrooms, teachers scan essays for cookie-cutter lines pulled from samples online. Grades drop when originality is low. The broader lesson is clear: repeating form signals lazy thinking. By mixing structure, word choice, and markup, a writer proves effort and earns authority. Breaking duplication is not extra work; it is the work.
What Makes Content Look Like AI
Large language models study billions of words, then predict common strings that likely belong together. As a result, AI output often shares clear tells. The first is uniform sentence length.

Every thought lands in a tidy fifteen-word line, marching like soldiers. Next comes flat rhythm: no short exclamations, few creative breaks, and little slang. Another sign is filler phrases such as
- “delve into“,
- “in the realm of“,
- or “moreover“
sprinkled every paragraph. Listicles appear with perfect symmetry: exactly three pros, three cons, each phrase starting with the same part of speech. In markup, AI tools love default heading ladders – H2, H3, H3 repeated again and again.
Image alt text may mirror the caption word for word. With time, readers grow familiar with these ticks. Educators and editors run machine detectors that flag them within seconds. Understanding the markers helps a writer dodge them. By varying length, tone, and layout, a human hand leaves unique fingerprints AI cannot mimic.
Crafting Natural Sentence Flow
Humans speak in waves, not in straight lines. One idea may sprint forward in five words. The next may wander for a while, painting a picture.
Mixing short and long sentences copies that breathlike motion on the page. A writer can test flow by reading the draft out loud. Stumbles signal places to trim, rearrange, or split clauses. Another handy trick is using action verbs. Instead of “The report was written by the team”, try “The team wrote the report”.
🗣️ Active voice moves faster and feels more alive. Transition words, such as “but”, “yet”, or “so”, guide the reader without sounding forced when used sparingly. Finally, occasional rhetorical questions or gentle humor can reset attention.
None of these moves require fancy vocabulary; they rely on rhythm. When sentences rise and fall like conversation in a coffee shop, AI detectors calm down, and readers lean in. Smooth flow is a simple cure for robotic tone.
HTML Editing
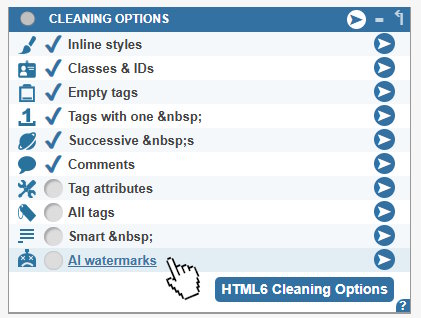
AI text generators often fill the text with special characters like — (—) or even invisible, hidden characters that AI text detectors can spot easily. Our online HTML editor has its built-in AI watermark remover, but only for subscribers at HTML6.com:
This new HTML cleaning option removes AI watermarks instantly with a click of a button.
Diversifying Vocabulary Without Jargon
Unique word choice can lift a post, yet rare terms may confuse middle-school readers. The balance sits in using everyday nouns and verbs while sprinkling in colorful but clear synonyms. A helpful exercise is building a word bank for the topic. List common industry phrases on one side, then write two or three plainer options beside each. When drafting, select different items from the bank so no single phrase repeats too often. Another tip is leaning on sensory language. Instead of “very cold“, write “ice cold“, “numbing“, or “freezing“.
Specific images stick better than intensifiers like “very” or “extremely“. However, caution remains vital; long Latin roots and hard science terms break rhythm. If a technical word is required, adding a brief parentetical definition keeps the flow smooth. Finally, watch clichés like “game changer” or “outside the box“. Swapping them for fresh comparisons shows a thinking mind at work. Varied vocabulary signals human care and kills copy-and-paste vibes.
Structuring Headings and Subheadings
Markup tells search bots how ideas connect. When every post uses the same heading ladder: H1, five H2s, then bullet lists. Machines sense automation. Swapping patterns helps. A writer might begin with an H2 question, follow with a short paragraph, insert an H3 list, and end with a storytelling blockquote. Another day, the plan could reverse.
<h1>Main title</h1>
<h2>Subheading</h2>
<h3>Sub-subheading</h3>
Consistency inside each single post matters, yet variety across the site keeps things fresh. Heading text should also shift. Instead of “Benefits of X” appearing in ten articles, try “Why X Still Matters” or “Hidden Perks of X“. Clear but playful subheads draw eyes and signal a living voice. In code, adding anchor links or id attributes sparingly can aid navigation without looking templated. Alt text for images should reflect the unique photo rather than echo the heading. By treating markup as part of the craft, not a rigid shell, a blogger reduces the AI feel of the whole page.
Mixing Up Media and Format
Readers crave more than plain text. Slideshows, short videos, hand-drawn doodles, and audio clips make a page feel handmade. Rotating media types also breaks the fingerprint many AI tools leave.
Most generators spit out only words and, at most, stock images. When a blog swaps in a five-second GIF or an embedded poll, pattern detectors hesitate. Interactive elements like quizzes invite clicks and time on page, another signal of human care. Still, balance matters; stuffing ten widgets into one article slows load speed and annoys phones on weak data. The smart move is choosing one or two fresh formats that support the core idea. A cooking post might add a looping clip of dough rising. A tech review could show a 360-degree product spin. Each extra piece needs alt text and captions that differ from main headings. By treating media as part of the story, not decoration, writers keep readers guessing and engaged.
Fact-Checking and Citing Sources
AI models sometimes hallucinate facts or mash together numbers from old data. When a post repeats those errors, trust vanishes. A careful writer compares every claim with at least two reliable sources. Government sites, respected journals, and first-hand interviews rank high. Adding a short citation in parentheses or linking a footnote shows openness, something bots rarely display.
Quotes should come from real people with clear roles, not generic “industry experts“. Including a brief bio after a name – “Dr. Lin, marine biologist at Pacific University” – gives weight.

Dates matter too; stating when a study was published guards against stale insights. While checking facts, the author can also test for logical flow: Does the result follow from the data? If not, rewrite. These small acts of verification create a textured voice that AI cannot fake. Readers sense diligence, and search engines reward accuracy, making fact-checking both moral and strategic. Over time, that habit grows authority and loyal readership.
Editing with Human Touch
Revision turns rough notes into polished stories. A screen reader or printout can shake loose hidden flaws that pass silently online. During the first edit, a writer checks structure: Does each section answer the promise made in the heading? The second pass inspects word choice and rhythm.
Reading backward, sentence by sentence, helps catch duplicate phrases. A third review focuses on formatting quirks – extra spaces, mismatched quotes, stray tags. Many AI detectors mark texts that end too neatly with a perfect summary line.
Adding an unexpected detail or a gentle joke in the closing paragraph shows a beating heart❤️ behind the keys. Beta readers also bring fresh eyes. Asking a peer to mark confusing parts highlights blind spots. Finally, letting the draft rest overnight allows the mind to reset. The next morning, weak spots glow like neon. Layered editing may sound slow, yet it saves time later when search bots and humans reward quality.
Ongoing Habits to Stay Original
Originality grows from routine, not random sparks. Setting aside ten minutes each day to read outside one’s niche feeds new ideas. Science journals, travel diaries, and comic strips all plant seeds that bloom later in blog posts.

Keeping a swipe file of striking phrases or structures – along with notes on why they work – makes future drafting faster and fresher. Another habit is rotating writing locations. A change from desk to park bench can shift mood and language. Monthly audits of published work help spot creeping repetition. If the same opener appears three times, retire it. Scheduling tool reminders ensure older articles get updated facts and new media, signaling ongoing care.
Finally, celebrating small experiments, like a poem-style section or a mini-podcast insert, encourages courage. These steady practices form a cycle: absorb, attempt, assess, adjust. Over months, the blog evolves in the only direction machines struggle to copy – forward. Such momentum shields creativity from stale, automated echoes.